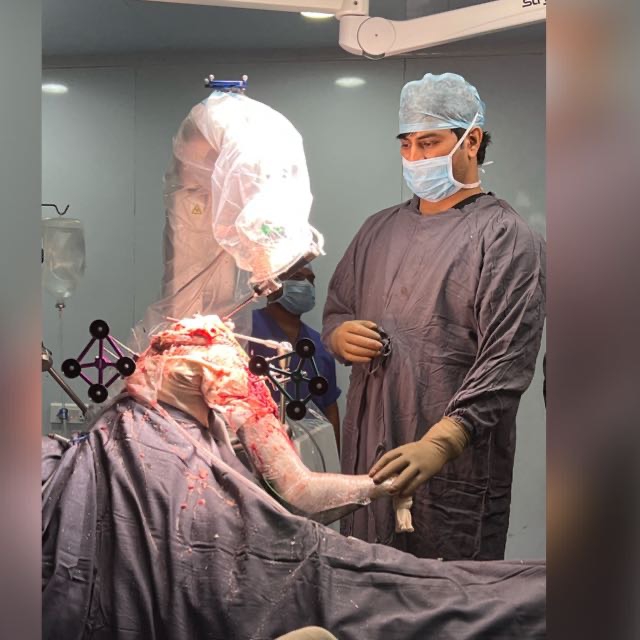
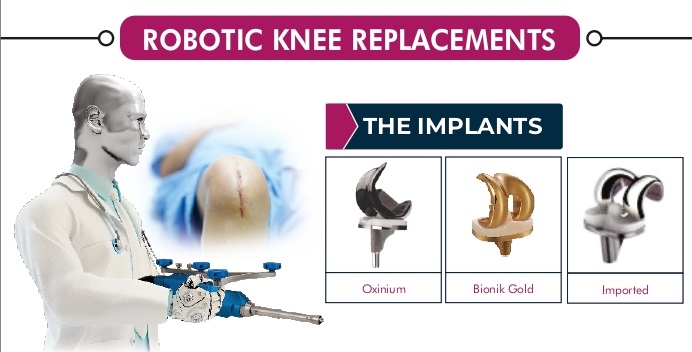
Robotic knee replacement surgery, also known as robot-assisted knee replacement, is a type of minimally invasive surgery that uses a specialized robotic arm to assist the surgeon during the procedure. The robotic arm is controlled by the surgeon using a computer console, which provides a high degree of precision and accuracy in placing the knee implant.
During the procedure, the surgeon makes small incisions in the knee and inserts the robotic arm, which is equipped with a camera and other instruments. The robotic arm is programmed to create a 3D virtual model of the patient’s knee, allowing the surgeon to visualize the joint and plan the placement of the implant.
The robotic arm then guides the surgeon in removing damaged tissue and bone and placing the implant in the correct position. The computer console provides real-time feedback to the surgeon, allowing for adjustments to be made as necessary.
Robotic knee replacement surgery offers several potential benefits over traditional knee replacement surgery, including:
- Greater accuracy and precision in implant placement, which can lead to a better fit and longer-lasting results.
- Reduced risk of complications such as infection, blood loss, and nerve damage, due to the smaller incisions and less invasive approach.
- Faster recovery time and less pain, due to the reduced trauma to the surrounding tissue and muscles.
However, robotic knee replacement surgery is not suitable for everyone, and it may not be covered by insurance in all cases. It’s important to talk to your doctor to determine if this type of surgery is right for you.
Robotic knee replacement is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that uses a robotic arm to assist in the placement and alignment of an artificial knee joint. The robotic arm is guided by a computer system, which allows for greater precision and accuracy in the positioning of the new joint.
Traditional knee replacement surgery is performed manually by the surgeon, while robotic knee replacement uses a computer-controlled robotic arm to assist in the placement and alignment of the new joint. This can result in greater accuracy and precision, as well as smaller incisions and less damage to surrounding tissue.
Candidates for robotic knee replacement are typically those who are experiencing pain and stiffness in the knee joint due to conditions such as arthritis, and have not found relief from other treatments. A doctor will evaluate each individual case to determine if robotic knee replacement is appropriate.
Benefits of robotic knee replacement include greater accuracy and precision in the placement of the new joint, smaller incisions, less damage to surrounding tissue, and potentially faster recovery times.
Recovery after robotic knee replacement surgery typically involves a period of physical therapy and rehabilitation to help restore strength and range of motion in the knee joint. Most patients are able to resume normal activities within a few weeks to a few months following surgery.
As with any surgical procedure, there are risks associated with robotic knee replacement surgery, including infection, blood clots, nerve damage, and allergic reaction to anesthesia. However, the use of robotic technology may help to minimize these risks.
The longevity of a robotic knee replacement can vary depending on a number of factors, including the patient’s age, activity level, and overall health. However, most artificial knee joints last between 20 and 30 years before requiring replacement.

